- 원본 논문 링크: https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.04606
1. Introduction
Continuous representations of words 학습에 관한 연구는 1988년부터 지속적으로 이어져왔습니다. 하지만 이전 연구들은 parameter sharing 없이 각 단어를 distinct vector로 표현하였고 단어의 internal structure를 고려하지 않아 morphologically rich language에 대해서는 좋은 word representation 학습이 이루어지기 어려웠습니다.
따라서 해당 논문은 다음을 하고자 합니다.
In this paper, we propose to learn representations for character n-grams, and to represent words as the sum of the n-gram vectors. Our main contribution is to introduce an extension of the continuous skipgram model (Mikolov et al., 2013b), which takes into account subword information. We evaluate this model on nine languages exhibiting different morphologies, showing the benefit of our approach.
2. Related Work
1) Morphological word representation
최근에 word representation에 형태학적 정보를 포함하려는 많은 방법들이 제안되었습니다.
- Alexandrescu and Kirchhoff (2006): factored neural language models (words are represented as sets of features)
- Lazaridou et al. (2013), Luong et al. (2013), Botha and Blunsom (2014), Qiu et al. (2014): morphemes(형태소)에서 representations of words가 파생되도록 하는 composition functions 제안
이러한 방식들은 단어들의 형태소 분리 (morphological decomposition)에 의존하나 논문에서 제안한 방식은 이에 의존하지 않습니다.
- Schütze (1993): singular value decomposition을 통해 representation of character four-grams 학습 & four-grams representations를 더해서 representation of words를 얻음
이는 논문에서 제안한 방식과 가장 유사한 방식입니다.
2) Character level features for NLP
이는 단어로 분할하는 것에서 벗어나 문자(character)에서 바로 language representations를 학습하는 것을 목표로 합니다.
- Recurrent neural networks: language modeling, text normalization, part-of-speech tagging, parsing
- Convolutional neural networks: part-of-speech tagging, sentiment analysis, text classification, language modeling
- Sennrich et al. (2016), Luong and Manning (2016): machine translation에서 subword units을 사용하여 많이 존재하지 않는 단어들의 representation을 얻는 방식을 제안
3. Model
강의 때 설명 예정
4. Experimental setting / Results
1) Experimental setting
C의 skipgram, cbow 모델과 비교
Optimization
- Stochastic Gradient Descent
- training size = T
- # of passes over the data = P
- time = t
- 𝛾_0이 fixed parameter일 때 step size = 𝛾_0 (1−𝑡/𝑇𝑃)
Implementation details
- word vectors dimension = 300
- negative samples = 5 (for each positive example)
- context window size = c (uniformly sample the size c between 1 and 5)
- rejection threshold = 1e-4
- keep the words that appear at least 5 times in the training set
- 𝛾_0=0.025 (skipgram), 𝛾_0=0.05 (cbow, our model)
2) Results
(1) Word similarity
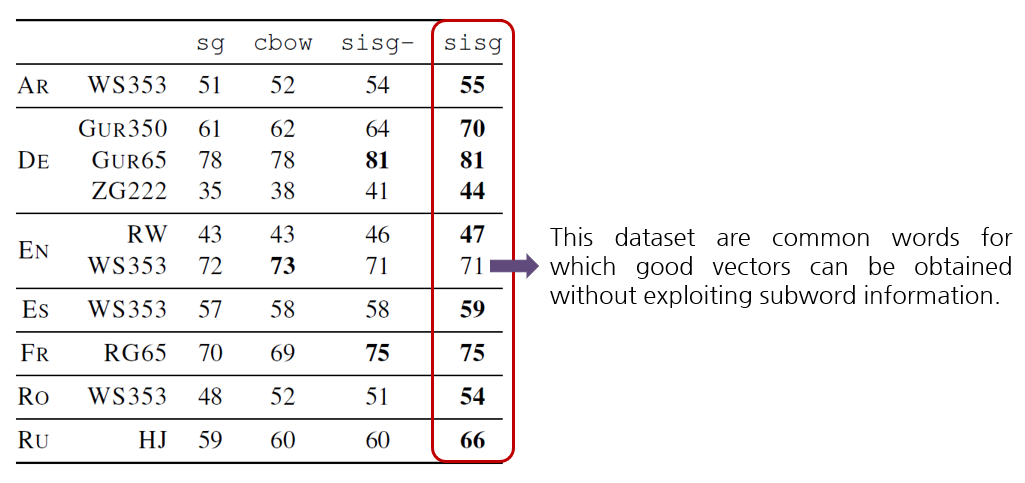
Human judgement와 cosine similarity between the vector representations의 Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient를 측정합니다. 그러나 training data에 나타나지 않는 단어들(out-of-vocabulary)의 representation은 skipgram이나 cbow를 사용해서는 구할 수 없습니다. 결과 비교를 위해 이러한 단어들에는 기본 값으로 null vectors를 부여하였습니다. 이 때의 모델 이름은 ‘sisg -‘ 입니다. fastText를 사용하면 OOV 단어들에 대해서 각 단어의 n-gram vectors를 더함으로써 valid representation을 구할 수 있습니다. 이 때의 모델 이름은 ‘sisg (Subword Information Skip Gram)’ 입니다.
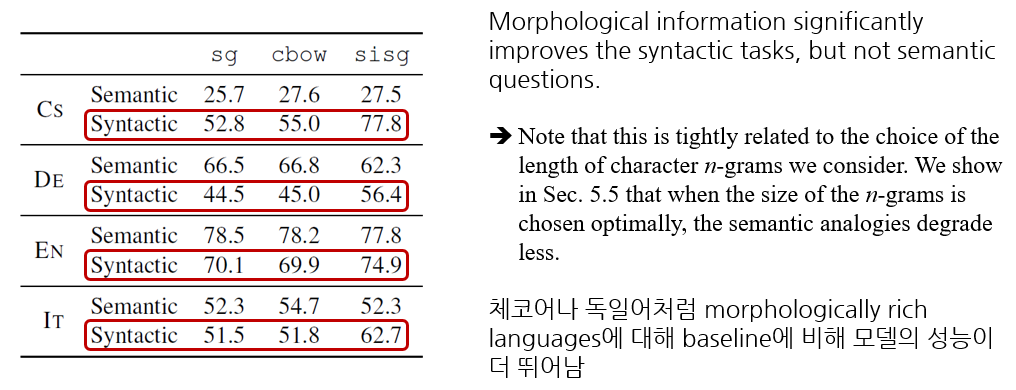
(2) Word analogies
We conducted evaluation on word analogy questions of the form A is to B as C is to D, where D must be predicted by the models
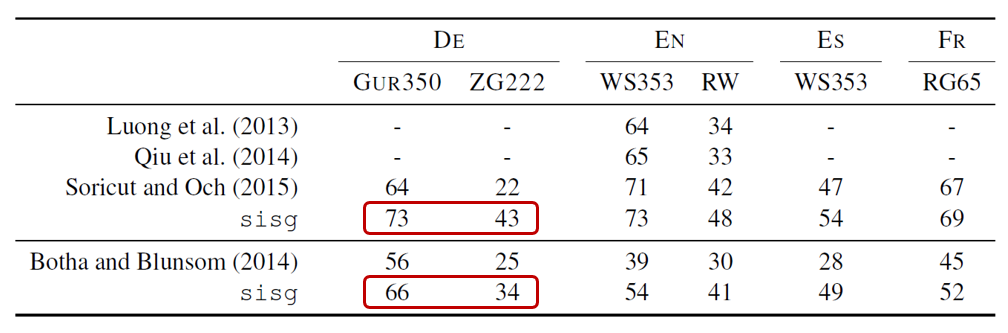
(3) Comparison with morphological representations
다음의 연구들과 이 논문의 연구를 word similarity task에 대해서 비교해보았습니다. 비교하려는 모델이 사용한 동일한 dataset으로 이 논문의 모델을 학습시켰습니다.
- Luong et al. (2013) – recursive neural network
- Oiu et al. (2014) – morpheme cbow
- Soricut and Och (2015) – morphological transformations
- Botha and Blunsom (2014) – log-bilinear language model
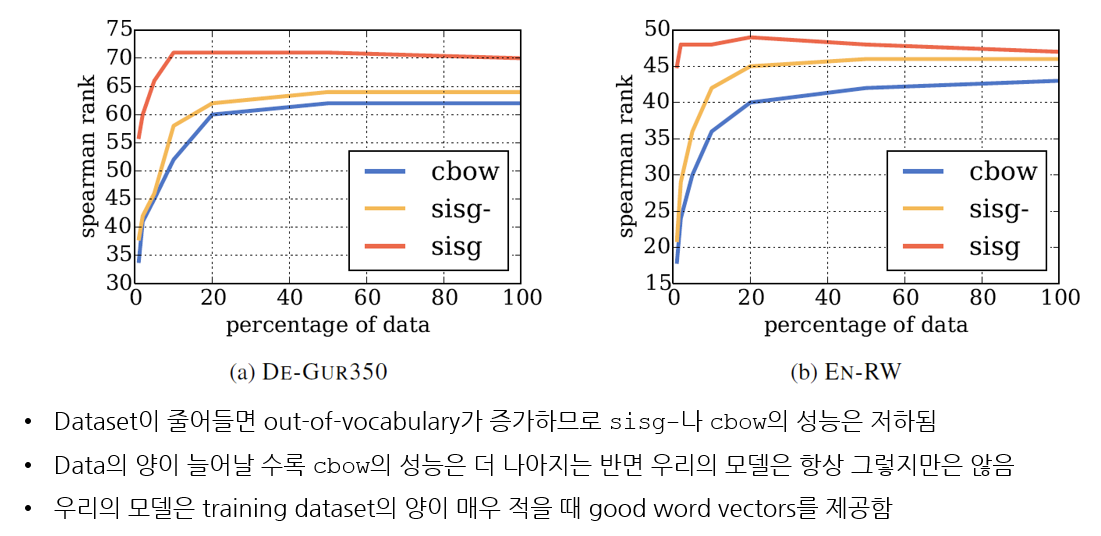
(4) Effect of the size of the training data
Training data size를 바꾸어 가며 similarity task에 대한 모델의 성능을 측정해보았습니다. 이 때 비교 모델로는 cbow baseline을 사용하였고, Wikipedia corpus를 처음 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 그리고 50% 만 사용하여 모델을 학습시켰습니다. (no reshuffle of the dataset)
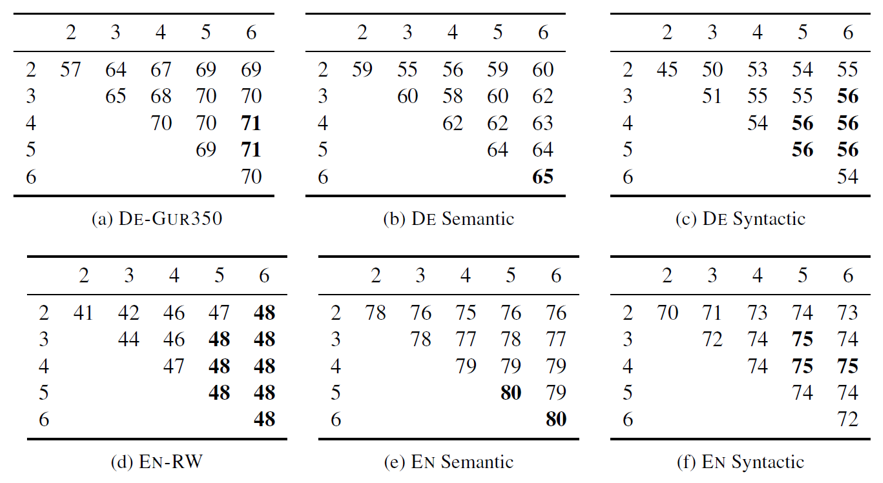
(5) Effect of the size of n-grams
앞서 Section 3.2 Subword models에서 언급했듯이 이 논문에서는 3~6까지의 n-grams를 사용하였습니다.
5. Qualitative analysis
1) Nearest neighbors
이 논문에서 제시한 모델과 skipgram baseline으로 학습된 vertors와의 cosine similarity를 이용하여 nearest neighbors를 찾아서 비교해보았습니다. 결과에서도 알 수 있듯이 논문의 모델이 복잡하고 기술적이고 잘 등장하지 않는 단어들의 nearest neighbors를 더 잘 찾아냅니다.
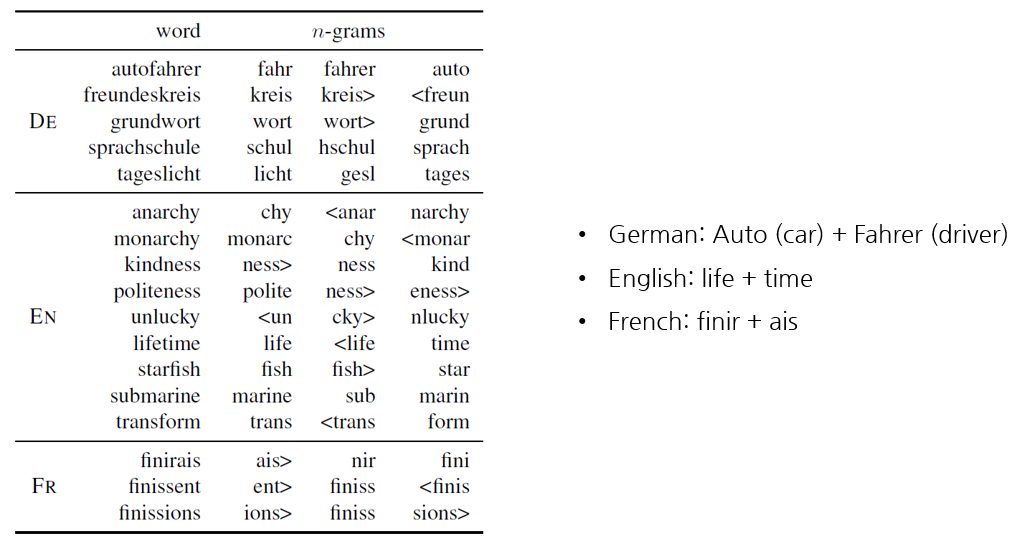
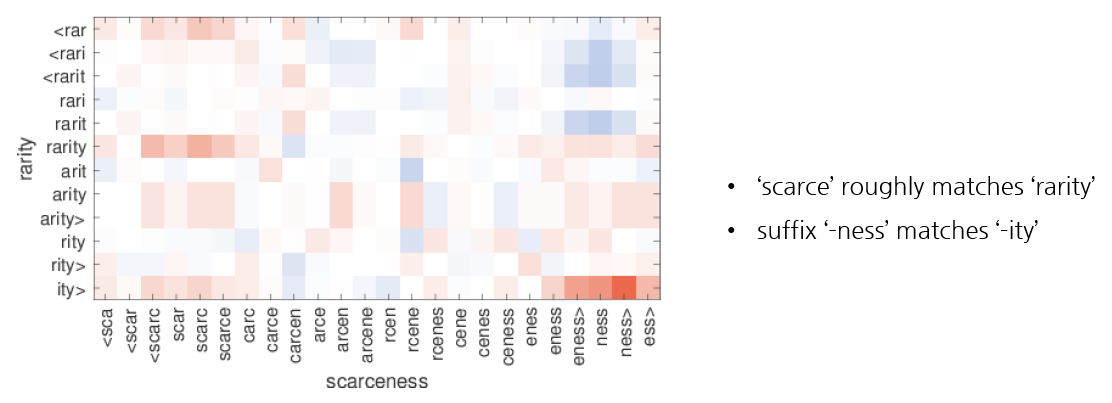
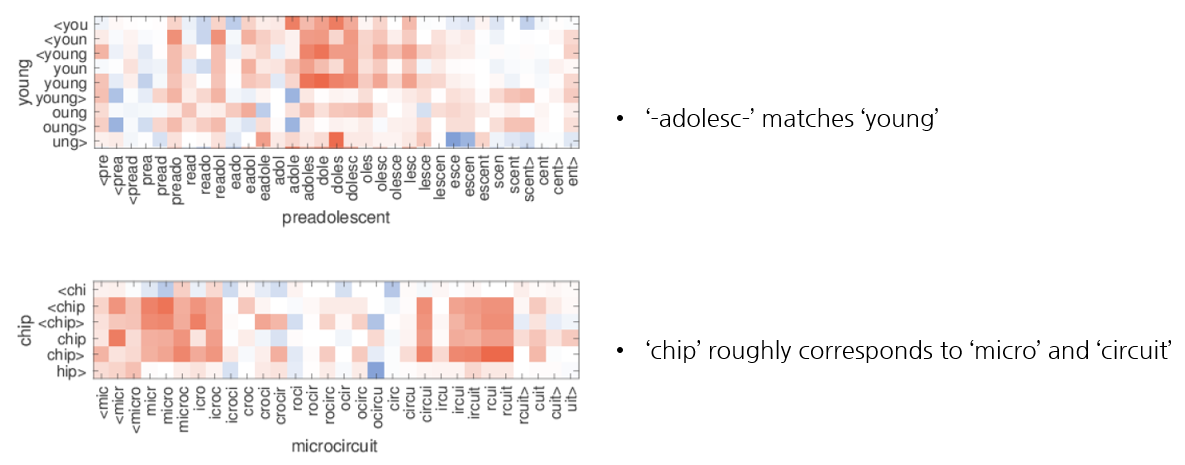
2) Character n-grams and morphemes
한 단어에서 가장 중요한 n-grams가 형태소에 해당하는지 확인하기 위해 해당 단어(즉, n-grams의 합)와 해당 단어의 n-grams g에 대해 g를 제거한 것의 cosine을 비교하여 그 값이 높은 순서대로 n-grams에 순위를 매깁니다. 그 결과는 아래와 같습니다.
3) Word similarity for OOV words
이 논문의 모델은 training set에 등장하지 않는 단어들에 대해 해당 단어들의 n-grams의 평균을 냄으로써 vector representation을 만들 수 있습니다. 이러한 representations를 평가하기 위해 training set에서 OOV와 유사한 단어의 n-grams와 OOV의 n-grams의 cosine similarity를 살펴보았습니다.
6. Conclusion
This paper investigate a simple method to learn word representations by taking into account subword information. This paper’s approach incorporates character n-grams into the skipgram model. This model trains fast and does not require any preprocessing or supervision.